Book Value vs Market Value: What’s the Difference?

They may also think the company’s value is higher than what the current book valuation calculation shows. The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share. The book value per share is calculated using historical costs, but the market value per share is a forward-looking metric that takes into account a company’s earning power in the future. With increases in a company’s estimated profitability, expected growth, and safety of its business, the market value per share grows higher. Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions. Consider technology giant Microsoft Corp.’s (MSFT) balance sheet for the fiscal year ending June 2023.
BVE Calculation Example
Additionally, the company had accumulated minority interest of $6.49 billion. After subtracting that, the net book value or shareholders’ equity was about $84.07 billion for Walmart during the given period. Suppose that XYZ Company has total assets of $100 million and total liabilities of $80 million. If the company sold its assets and paid its liabilities, the net worth of the business would be $20 million.
The Difference Between Market Value per Share and Book Value per Share
Outdated equipment may still add to book value, whereas appreciation in property may not be included. If you are going to invest based on book value, you have to find out the real state of those assets. That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company. In some cases, a company will use excess earnings to update equipment rather than pay out dividends or expand operations. While this dip in earnings may drop the value of the company in the short term, it creates long-term book value because the company’s equipment is worth more and the costs have already been discounted. An investor looking to make a book value play has to be aware of any claims on the assets, especially if the company is a bankruptcy candidate.
Companies Suited to Book Value Plays
The difference is due to several factors, including the company’s operating model, its sector of the market, and the company’s specific attributes. The nature of a company’s assets and liabilities also factor into valuations. The increased importance of intangibles and difficulty assigning values for them raises questions about book value.
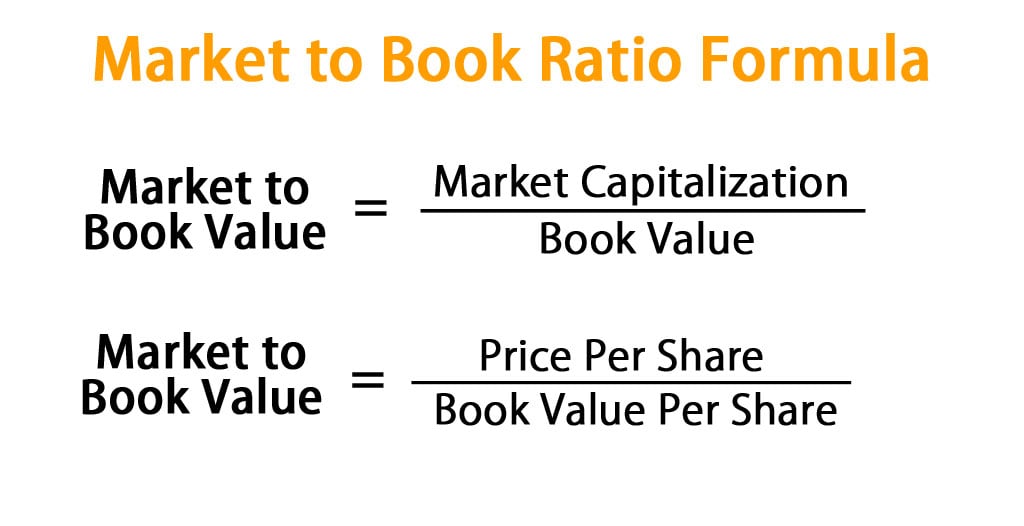
If the book value per share is higher than its market value per share then it can indicate an undervalued stock. If the book value per share is lower than its market value per share, it can indicate an overpriced, or overvalued stock. When the market value is near or less than the book value, the P/B ratio will be 1 or less, signaling that the stock may be undervalued. An undervalued stock can be a great bargain, particularly if company fundamentals are strong and the investor has a long timeline. Investors commonly analyze book value in the context of the company’s market value.
Measuring Book Value Per Share (BVPS)
For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns. U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require marketing costs to be expensed immediately, reducing the book value per share. However, if advertising efforts enhance the image of a company’s products, the company can charge premium prices and create brand value. Market demand may increase the stock price, which results in a large divergence between the market and book values per share. The BV of equity is a useful valuation tool to identify overvalued and undervalued stocks.
People who have already invested in a successful company can realistically expect its book valuation to increase during most years. However, larger companies within a particular industry will generally have higher book values, just as they have higher market values. That may justify buying a higher-priced stock with less book value per share. The market value represents the value of a company according to the stock market.
Next, the “Treasury Stock” line item captures the value of repurchased shares that were previously outstanding and available to be traded in the open market. The book value of equity will be calculated by subtracting the $40mm in liabilities from the $60mm in assets, or $20mm. There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company. This differs from the book value for investors because it is only used internally for managerial accounting purposes. A negative book value means that a company’s liabilities are greater than its assets.
- The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- That leads to a book valuation of $206.22 billion ($411.97 billion – $205.75 billion).
- Typically, the market value almost always exceeds the book value of equity, barring unusual circumstances.
- In those cases, the market sees no reason to value a company differently from its assets.
It is a dollar amount computed based on the current market price of the company’s shares. When the market value is greater than the book value, the stock market is assigning a higher value to the company due to the earnings power of the company’s assets. In comparison, the market value of equity refers to how much the common equity of a company is worth according to the latest prices paid for each common share and the total number of shares outstanding. The figure that represents book value is the sum of all of the line item amounts in the shareholders’ equity section on a company’s balance sheet. As noted above, another way to calculate book value is to subtract a business’ total liabilities from its total assets.
Book value is the value of a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits divestiture definition to buy more assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. If, for example, the company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, common equity increases along with BVPS. On the other hand, if XYZ uses $300,000 of the earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases.
Market values for many companies actually fell below their book valuations following the stock market crash of 1929 and during the inflation of the 1970s. Relying solely on market value may not be the best method to assess a stock’s potential. It had total assets of about $252.39 billion and total liabilities of approximately $161.83 billion for the fiscal year ending January 2024.
Leave a reply →